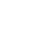What is Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)?
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is an optical analog of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) that can be used to examine the coronary arteries and has 10-fold higher resolution than IVUS. It is a new, non-invasive imaging technique that generates volumetric angiography images in a matter of seconds.
So how does OCT procedure work?
OCT uses near-infrared light to create images of the inside of the coronary arteries delivering very high-resolution images. A beam of light is directed at the artery, and some of the light reflects from inside the artery tissue and some of it scatters. This scattered light causes something called “glare.”
OCT also lets cardiologists clearly see the plaque inside an artery, find out how much fat or clot is inside an artery, and take precise measurements before and after placing stents.
What is Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR)?
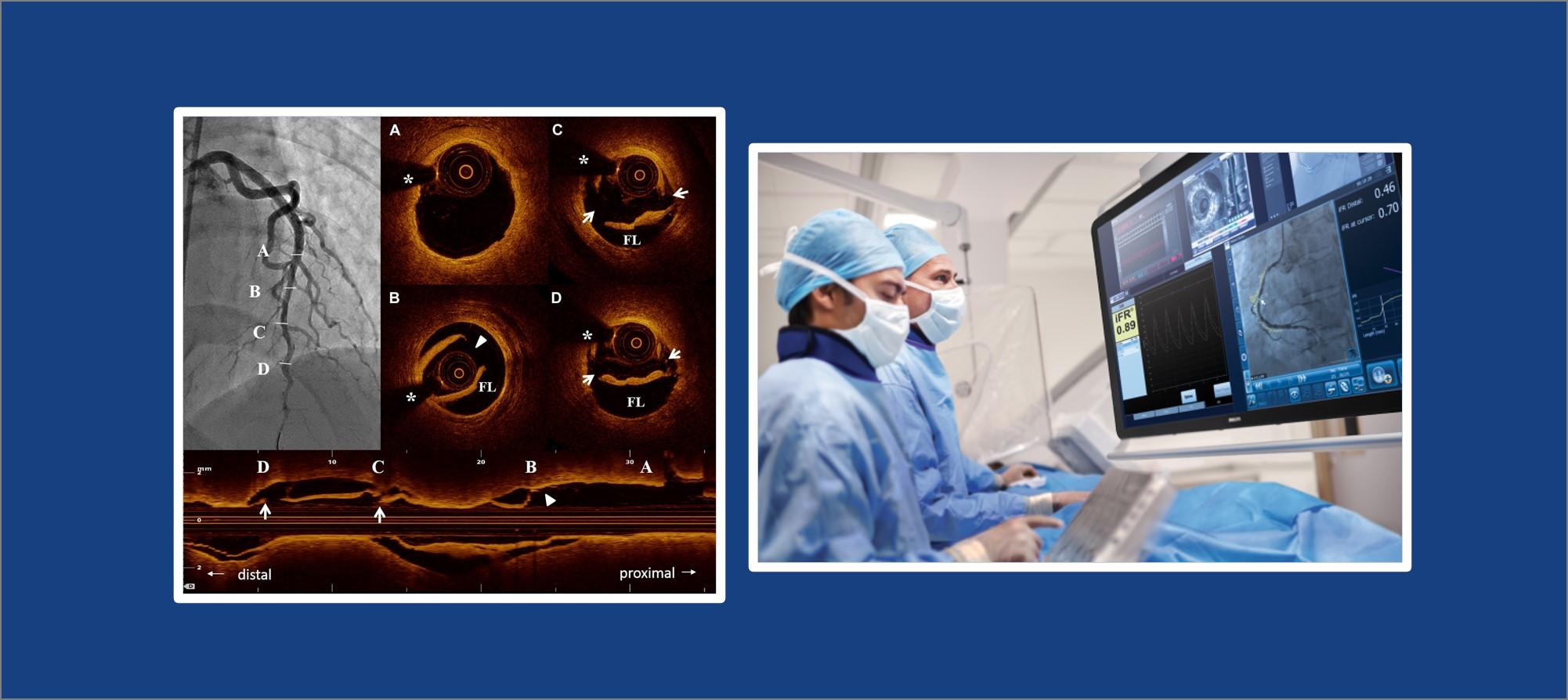
Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) offers yet another tool to assist in identification of those intermediate blockages. It is a guide wire-based procedure that can accurately measure blood pressure and flow through a specific part of the coronary artery. FFR is done through a standard diagnostic catheter at the time of a coronary angiogram.
So how does the FFR procedure work?
FFR is usually measured following coronary angiography in the catheterization laboratory. A guiding catheter, a pressure monitoring guidewire, and a hyperemic stimulus are required for the FFR measurement.
Although a diagnostic catheter (4 Fr or 5 Fr) is feasible, it is recommended that a normal guiding catheter should be used to perform FFR not only for easier handling but also for rapid access with balloons or stents in the rare event of vessel dissection or perforation.
Results are displayed on a special monitor (left) along with the “FFR value”. Studies have shown that an FFR value less than 0.75 or 0.80 corresponds to inducible ischemia, and most likely will require interventional treatment. Blockages that score above this threshold can be safely and adequately treated by medical therapy without the need for angioplasty.