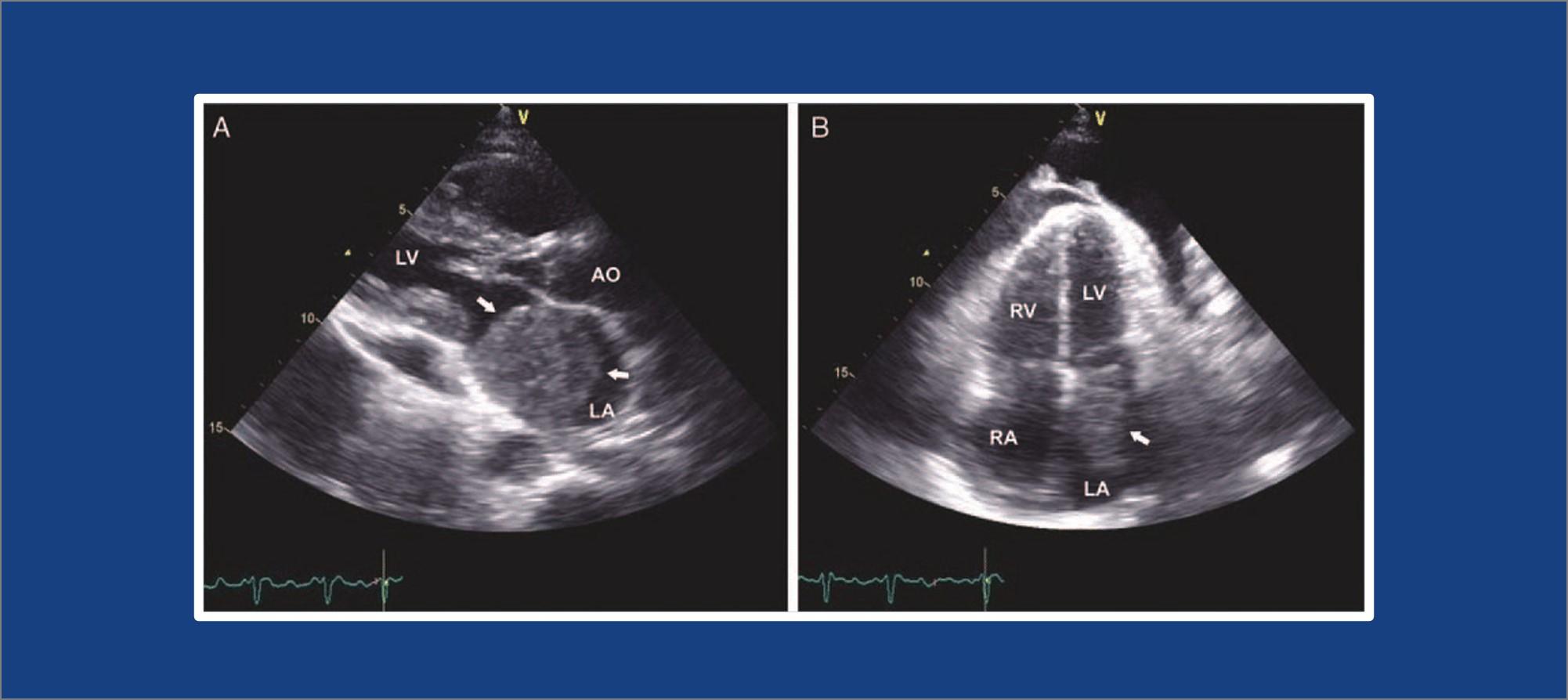
What is an echocardiography (or echo)?
An echocardiography is a test that uses ultrasound to make pictures of your heart and show how your heart muscle and valves are working. The sound waves make moving pictures of your heart so that your cardiologist can look at the shape and size.
You might have heard calling this procedure simply “echo” or sometimes echocardiogram.
Why do I need an echocardiography?
An echocardiography is the key in determining the health of your heart muscle, especially after a heart attack. It can also reveal heart defects in unborn babies.
Basically, your cardiologist orders an echocardiography to:
- Look for any heart disease
- Look for heart valve disease
- See how medical/surgical treatments are working
- To see your heart pumping strength
- Detect any clots in the heart chambers
- See any fluid in the sac around the heart
- See if blood is leaking backwards through your heart valves (regurgitation)
- Check if there is a tumor or infectious growth around your heart valves
Is there any risk?
An echo can’t harm you. An echo doesn’t hurt and has no side effects.
During echocardiography
Most echocardiography takes less than an hour and can take place in a hospital or doctor’s office.
- You lie on a table and a technician places small metal disks (electrodes) on your chest.
- These disks have wires that are connected to an electrocardiograph machine.
- ECG or electrocardiogram keeps track of your heartbeat.
- Your technician puts gel on your chest so that sound waves pass through your skin.
- The transducer is passed across your chest which produces sound waves that bounce off your heart and echo back to the transducer.
- The sound waves are change into pictures and displayed on a video monitor.
This is called transthoracic echocardiography. It is the most common type of echocardiography. It’s painless and noninvasive.
Other types of echocardiography
Transesophageal echocardiography – This is carried out when the above procedure doesn’t produce definite images. In this procedure, the doctor guides a smaller transducer down your throat through your mouth. The doctor will numb your throat to make this procedure easier and eliminate the gag reflex.
Stress echocardiography – This is done using the traditional transthoracic echocardiography. However it is carried out before and after you have done exercise to make your heart beat faster.
3D echocardiography – To create a 3-D image of your heart. This involves multiple images from different angles. It’s used prior to heart valve surgery.
Fetal echocardiography – Fetal echocardiography is used on pregnant mothers during weeks 18 to 22 of pregnancy. The transducer is placed over the woman’s abdomen to check for heart problems in the fetus.
Recovery after an echocardiography
Generally, there is little to no recovery time needed for an echocardiogram. For transesophageal echocardiogram, you may experience some throat soreness after the procedure but it should go away within about 2 hours.